Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing Spondylitis
What is it?
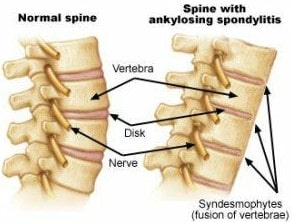
Ankylosing Spondylitis is a chronic, or long-lasting, disease that primarily affects the spine and may lead to stiffness of the back. The joints and ligaments that normally permit the back to move become inflamed. The joints and bones may fuse together. It is a type of a group of diseases called Spondyloarthritis (SPA).
What causes it?
The cause is unknown but genetics seems to play a role. A gene called HLA-B27 occurs in 90 percent of those with ankylosing spondylitis. Just because you have the gene, does not mean you will have ankylosing spondylitis. Other factors besides HLA-B27 are involved leading to immuno-inflammatory damage.
What are affected?
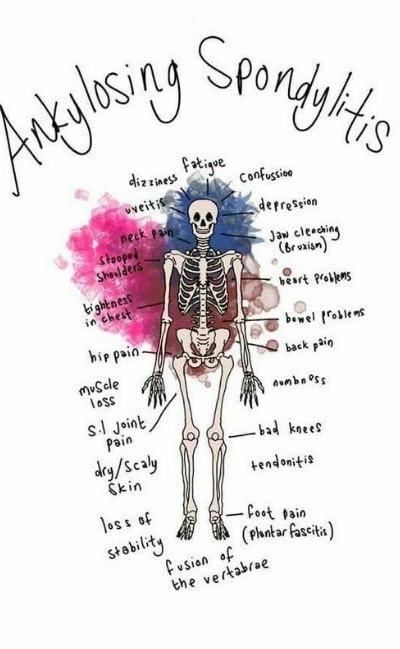
- AS causes inflammation (joint pain and swelling)
- The most common symptoms are chronic pain and stiffness in the lower back which usually starts where the lower spine is joined to the pelvic bone.

What are the types?
It may be primary ankylosing spondylitis or secondary like Psoriatic SPA, Inflammatory bowel disease-related, reactive and undifferentiated SPA.
Treatment options
With early diagnosis and treatment, pain and stiffness can be controlled and may reduce fusing. In women, Ankylosing Spondylitis is usually rare and difficult to diagnose.
Treatments may include:
- Exercise, especially swimming
- Medications: NSAIDs, sulfasalazine & Methotrexate
- Biological agents like TNF Blockers (Infliximab, Etanercept, Adalimumab & Golimumab)
- Posture management
- Self-help aids
- Surgery
The principles of treatment of ankylosing spondylitis are to control the inflammation so that scarring and calcification with subsequent stiffening of the spine and of joints are minimized as much as possible.
The usual anti-inflammatory drugs that are used for other forms of arthritis are utilized here as well, such as NSAIDs and COX-2 inhibitors. Corticosteroids, which play a larger role in rheumatoid arthritis, play less of a role in ankylosing spondylitis. However, when a single joint is affected, it may be injected by the physician or rheumatologist for easier rehabilitation. Drugs Like sulphasalazine, methotrexate and biological agents like etanercept or infliximab are useful therapeutic agents for long term treatment.
Who is at risk?
Although both men and women get ankylosing spondylitis, it primarily affects men. Onset usually occurs between 17 and 35 years but can occur in children and in older age groups.
Other complications:
It can affect eyes (Uveitis), Lung (fibrosis), nervous systems (Paralysis), cardiac (valve or coronary disease), Kidney (nephritis), etc.
If treated well from early, the overall outcome is good. Surgery for bad hips/knees improves quality of life. Physiotherapy like swimming is very useful.
